Cyber Warfare: The New Threat by Air Marshal AKTiwary in IDR 14/12/2012
The cyber warriors will identify own
networks weakness which will be followed up by regular patch up of
vulnerabilities. In addition their actual target could include blowing up
electric generators / motors; use of high power microwave to upset fly by
control of combat aircraft and more.
Some contemporary
thinkers have equated Cyber-Warfare as another new form of warfare which is on
par with Land, Naval and Air Warfare. This is partly reflected in USA creating a
new Cyber Command headed by a General, who is also the boss of Central Security
Services and Director of National Security Agency. In the 2010 strategic review
of security and defense in UK, while many major defense programmes have been cut
and overall defense budget is reduced by eight percent, Cyber War has been
allotted £ 650 m for the period 2010-14. A significant increase
indeed!
Cyber War has become a major subset of warfare now, because the
militaries and their equipments rely on many systems, each of which has
computers, often many computers in each system.
While Cyber War
seems a very familiar term to everyone, it will be useful to revisit its
characteristics which make it so important and so different from other forms of
warfare. It is distinctly different from the traditional warfare wherein armies,
navies and air forces are massed against each other to fight one
another.
Cyber War can be
fought by anyone; even an individual using his hacking skills against huge
corporations, nations or even different civilizations. One single person’s
malicious software can wreck havoc on computer networks and programmes spread
across nations and continents. The modem world’s industry, economy, institutions
and even other facets of life is supported by computers and associated software.
So all these facets of life can be disrupted for prolonged period by cyber
attacks. The individual could be -acting alone; he could be part of a group
pursuing its inimical agenda or could be state supported, working to further the
plans of the state. The defender cannot distinguish between them or pinpoint the
full identity of the attacker or the actual source of attack. So while the cyber
enemy may be guessed, definite, pinpointing is nearly
impossible.
Amongst various
types of warfare, cyber war is the cheapest option. At its simplest, all it
requires is one individual, on one computer to originate cyber attacks. There is
no need for regular massive cyber armies equipped with all the paraphernalia of
a conventional war; being trained, sustained and replenished regularly. Unlike
in conventional war, where the attacker generally suffers heavy casualties, in
Cyber War there is no casualty to the attacker. In this war, it is not the
physical might of a soldier, the quality and quantity of equipment, the
integration and orchestration of systems, or the strategic genius of a General
which is tested. It is only the computer genius and skills – and these too come
as easily to gifted teens as to the experts after years of serious study and
perseverance. Therefore, each and everyone cannot be a cyber warrior.
Conscription cannot create a Cyber Army — it is by recruiting suitable people
with aptitude for such work. In cyber force, there is not much place for officer
– soldier hierarchy. Rather it is a team of the like-minded.
The malware can be inbuilt in to the computer system at
manufacturing stage itself. It can be pre-designed in micro chips for various
items like sensors, routers, switches etc. It can be injected later on into
system as a sleeper cell.
When one’s computer
system does not work, it is not easy to distinguish whether the failure is a
genuine malfunction or a result of malicious attack. More often than not one
tends to believe that his computer system itself is malfunctioning. So it is
difficult to determine if one is under cyber attack. The nature of attacks are
such, for example hidden Trojans activated on command or at pre-determined time,
that one does not know when the actual attack was launched.
The origins of
attack also remain uncertain. The attacking nation or non-state actor can route
his attack via a computers located in a third country or even through benign
computers based in the country being attacked. These could be the personal
computers of citizens of the country under attack. Such an approach poses major
dilemma for defender and for the right to computer privacy in democratic
societies.
The malware can be
inbuilt in to the computer system at manufacturing stage itself. It can be
pre-designed in micro chips for various items like sensors, routers, switches
etc. It can be injected later on into system as a sleeper cell. Its algorithm
can be programmed in variety of ways to defeat most defenses.
The defender in
cyber world has to cope with many problems. The existing defenses are against
only known viruses/worms. Defense networks, therefore, require constant
upgradation. Even secure nets can be injected with virus even though attacker is
not physically connected into the net. But then excessive security on the net
decrease the system speed.
Detailed information
on cyber war in various countries is difficult to find. However, certain amount
of information is available about development of cyber war organisation in USA
in the open literature. Hence it is proposed to study the evolution of cyber war
organisation in USA.
USA
In earnest
Electronic Warfare (EW) started during World War II. It matured as the radars
and radar guided SAMs and anti-ac artillery evolved through the Vietnam war; the
wars in the Middle East etc, Till recently EW meant brute jamming of signals or
breaking the electronic lock on an aircraft by moving the lock away spatially.
In the Op Desert Storm of Gulf War 91, false target information was injected
into Iraqi Integrated Air Defence System, thereby misleading its computers. This
can be considered the start of Cyber War in military domain. The Cyber War in
the civil domain by way of unethical hacking into banking networks started
little earlier.
IW operations were undertaken during Bosnia Operation in 1995 and
against Serbia in 1999. The comprehensive operations included EW against Radars
and SAMs, cyber attacks against IADS, operations against Television, Radio as
well as cyber attacks against computer based systems like power generation, Oil
refining systems…
So now there are
three terms : EW, Cyber War and Information War often loosely used to convey the
same thing. Electronic War is said to take place when electrons in a system are
disturbed. Cyber space is also the space where electrons flow conveying
information. But cyber space is normally referred to space in which computer
electrons move around – either within the computer itself or between many
computers connected in a network. The network itself could be a cable or fiber
optic network or a wireless net in which electronic signals move between a
transmitter and a receiver — the most apt example being a satellite and its
terminals. Thus, in the militaries too, initially terms like EW, IW and Cyber
War were used loosely and interchangeably.
Cyber War has become
a major subset of warfare now, because the militaries and their equipments rely
on many systems, each of which has computers, often many computers in each
system. At the same time all facets of civil life, industry, banking and
financial service power generation etc have also been based on extensive
computer networks and infinite number of software lines. In such a huge complex
of electrons, EW as practiced till 1980s, forms a small subset. Altering cyber
electrons means altering information-hence the term IW. However, in current US
terminologies IW means irregular warfare. Cyber War includes the earlier EW and
IW.
Evolution of Cyber War
USAF set up IW
squadrons in 1980s. All banking institutions and major industries especially the
Aero Space industries also started building in cyber security in their networks.
The financial institutions were at the forefront of cyber attacks, wherein
hackers tried to steal/siphon money. This threat to banks and the security
precautions could not be made public in order to retain the investor
confidence.
As a result of
success of IW in the Gulf War 91, USAF decided on IW across full spectrum of
command and control. So the 688th Information Operations Wing was set up. The
Wing has technical skill sets of AF Electronic Warfare centre; AF Cryptographic
support center’s Securities directorate and Intelligence capabilities from
former AF Intelligence Command. As on 2010, it has a staff of 1000 which
includes military and civil.
…cyber space has data,
networks and electronic devices. Good cyber defense implies protecting all three
components and not merely data.
In 1993 USAF
established an IW Cell at Kelly Air Force Base, Texas. By mid 90s, the IW
flight, consisting 25 personnel, would work alongside Combined Air Operation
Centre (CAOC) whenever operations were going on. IW operations were undertaken
during Bosnia Operation in 1995 and against Serbia in 1999. The comprehensive
operations included EW against Radars and SAMs, cyber attacks against IADS,
operations against Television, Radio as well as cyber attacks against computer
based systems like power generation, Oil refining systems etc.
In the past, the US
caused a massive explosion in a new trans-Siberian oil pipeline running
from the Urengoi gas fields in Siberia across Kazakhstan, Russia and Eastern
Europe. It did it by causing its pumping station to over rev by computer malware
in cooperation with some outraged Canadians who had supplied the software
for the pumps.1 USN established its cyber cell in 1999 and mandated the unit to
become like the ‘Top Gun’ amongst fliers.
In Dec 1998 DoD/USAF
established Joint Task Force on Computer Network Defense ITF – CND. It was
headed by a Maj Gen and was to work with the Army, Navy and the Marine Corps.
This was an immediate result of a massive malware attack on US -military nets.
It took the US 14 months to clean up this virus from its systems. It also
revealed the enormity of possible damage to improperly secure
networks.
Cyber War exercises
named “Eligible Receiver” and “Solar Sunrise” were conducted in which Federal
Agencies/Services, Israeli analysts and Californian teens attacked Defense
networks. Weaknesses and vulnerabilities were identified and preventive steps
initiated. In Sep 2001 Pentagon created Joint Task Force-Computer Network
Operations- JTF-CNO. The replacing of CND by Computer Network Operations (CNO)
implied the need to attack in order to defend proactively.
In 2008 DoD defined
cyber space as, “a global domain within the information environment consisting
of interdependent network of information technology infrastructures, including
the Internet, telecommunication network, computer system and embedded processor
and controllers.” It illustrated that cyber space has data, networks and
electronic devices. Good cyber defense implies protecting all three components
and not merely data. Earlier, it was believed that encrypting data was enough
for cyber security.
Cyber Defense now
meant following:
Cyber security is akin to Air Superiority. One has to fight to
attain it and thereafter sustain it with constant effort. Also cyber security
relates to place and time. Unlike air war in which offense is the best defense,
in cyber war defense becomes primary…
- Secure and exclusive networks in which individuals cannot plug in Pen Drives, CDs and external devices.
- Defense in depth by firewalls. So that when under a cyber attack the system degrades gradually rather than suffer catastrophic collapse. And after attack is over, the system recovers.
- The system should be Self Diagnosing and to have built in healing capability.
- Data bases must employ stealth methodologies where for example, modulating chip technology enables them to hide, morph and masquerade as effectively as any attacking agent.2
Cyber security is
akin to Air Superiority. One has to fight to attain it and thereafter sustain it
with constant effort. Also cyber security relates to place and time. Unlike air
war in which offense is the best defense, in cyber war defense becomes primary
because of nature of attacker. There are no hostile cyber bases which preemptive
bombing can destroy.
In 2001 USAF placed
Cyber Wing under Space Command. By May 2002 it had a manning of 340 personnel.
Later Cyber Command was made a sub unit of US Strategic command. It achieved
full operational capability on 31 Oct 2010. The Cyber Command is headed by a
General who also is the Director National Security Agency (NSA) and Chief of
Central Security services. This arrangement in one stroke has made cyber
structure more horizontal and integrated. Cyber command looks after all military
networks numbering 15000 in all the Services. It has replaced the earlier Joint
Task Force – Computer Network Operating and the Joint Functional Component
Command for Network Warfare JFCC-NW. It has under it the Cyber Commands of US
Army, Navy, Marine Corps and Air Force. It is responsible for both defense and
offense in Cyber War. In addition it provides technical and electronic warfare
support to Department of Homeland Security (DHS). If and when asked by DHS it
will provide additional assistance. DHS looks after civil and private
networks.
…as the cyber process and attacks kept increasing, especially post
9/11 and after the incident of US spy plane P3C Orions collision with a Chinese
interceptor in which the Chinese pilot died, USA selected a new strategy for
cyber security.
NSA looks after all
the government networks apart from the ones in military domain. US CYBERCOM has
been tasked to develop:
- Methods to assess operational impact of intrusions.
- Identify proper response.
- Coordinate action with appropriate organizations.
- Prepare Response Plans.
- Execute plans through Service components.
US CYBERCOM will
also issue Operational Alert conditions depending upon detected threats. The
conditions are normal, A,B,C & D. Over and above these arrangements the
Cyber organizations seek support and rely on private security specialists
companies to deal with cyber threat.
The earlier concept
of cyber security was purely defensive. However, as the cyber process and
attacks kept increasing, especially post 9/11 and after the incident of US spy
plane P3C Orion’s collision with a Chinese interceptor in which the Chinese
pilot died, USA selected a new strategy for cyber security. Now it was felt that
purely defensive strategy was reactive and insufficient to ward off cyber
threat. For proper cyber security there is a need to actively patrol the cyber
network for detecting potential trouble. So the new strategy of cyber attack
comprises following:
- Denial of Service
- To patrol the Internet to pinpoint attackers.
- To create Logic bombs, worms, Trojans & Malware for use as and when needed.
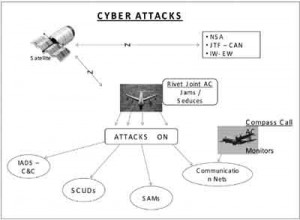
The diagram
illustrates the working of a computer network attack (CNA).3
Rivet Joint is an
specialist transport aircraft (KC-135) which is used for CNA. It is in contact
with ag
Agencies like NSA, JTF – CNA, and IW – EW centers via satellite links to
receive and send back latest information for CNA planning. It injects cyber
weapons as appropriate into hostile IADS network, Scud type missiles command and
control centre and the communication networks. Another special aircraft called
Compass Call (C-130 modified) monitors the effectiveness of communication
network attacks.
In USA 24th AF looks
after cyber operations, manned by 14000 airmen. The 24th AF has three major
wings and an operations centre under it. These are:
- 67th Network Warfare Wing: It looks after information operations. Its 8000 strong manpower is located at some 100 locations worldwide. There are 35 squadrons and these deal in operations of Television, Radio, Telephone exchange and networks including mobile phones and networks.
- 688th Information Operation Wing: Deals in cyber space R&D and manned by 1000 staff which is a mix of military and civil.
- 689th Combat Communication Wing: Its mission is to train, deploy and deliver expeditionary and specialized communication; air traffic and landing systems for relief and combat operations.
 In 2010
USAF undertook some important steps with regard to cyber branch. It established
a new cadre for Cyber War with 1000 cyber warriors. These personnel were
selected after a strict screening process which also judged their aptitude for
cyber work. Their performance in online games was also a major criteria. This
cadre is to be expanded to 6000. The cadre will comprise military, government
employees, contractors and willing patriotic youths. Specialist cyber strike
units will be created from these personnel. The training will include
undergraduate cyber training, initial qualification training. The standards,
evaluation and examinations will follow similar pattern as for flying training.
The cyber warriors will get incentive pay similar to flying pay. Their main
communication devices will be Droids and I Phones connected on secure and
non-secure networks.
In 2010
USAF undertook some important steps with regard to cyber branch. It established
a new cadre for Cyber War with 1000 cyber warriors. These personnel were
selected after a strict screening process which also judged their aptitude for
cyber work. Their performance in online games was also a major criteria. This
cadre is to be expanded to 6000. The cadre will comprise military, government
employees, contractors and willing patriotic youths. Specialist cyber strike
units will be created from these personnel. The training will include
undergraduate cyber training, initial qualification training. The standards,
evaluation and examinations will follow similar pattern as for flying training.
The cyber warriors will get incentive pay similar to flying pay. Their main
communication devices will be Droids and I Phones connected on secure and
non-secure networks.
The cyber warriors
will identify own networks weakness which will be followed up by regular patch
up of vulnerabilities. In addition their actual target could include blowing up
electric generators / motors; use of high power microwave to upset fly by
control of combat aircraft and more.4
The NSA and JFCC –
NW have worked together since 2005. The NSA has 700 personnel with Ph D. This
vast experience is shared by the other cyber warriors who have benefited
immensely. The CYBERCOM has partnership with 100 universities to train students
on net security. Many of these students, thereafter, join NSA or civil cyber
agencies. Now using the computer net attack, US forces can penetrate hostile
computers systems and either mine it for data or damage it with crippling
algorithms or even spoof it with false information. Some of the CNA tricks
include ringing hostile phones every 30 seconds; send a fabricated Fax directly
to the enemy operator to do things that would lead to trouble; sending
accusatory e-mails etc. The idea is to make the enemy distrust own communication
system or to shut down all communications.5
The Israelis
established in Umbrella C4I in Mar 2003. By 2007 all intelligence networks were
connected, sharing all sensor information. The network includes fixed sites as
well as mobile sites. During 2009 Gaza conflict Israeli Air Force down loaded
sensor imagery on U-tube; its tweets warned of rocket attacks and it used
‘help-us-win.com’ blog to mobilize public support.6
Placed below are the
recommendations with respect to Cyber War by a USAF study in 2008. The study was
undertaken to suggest needed reorganization within the USAF for 2018-2023 time
frame. Cyber War is a new domain for all the countries. It appears that USA and
China have a lead in Cyber War domain over India of about ten years. The
emphasis placed by them on cyber war is instructive for us to take
note.7
Cyberspace : Boundless Opportunity and Significant Vulnerabilities
- USAF must not focus solely on protecting its databases, but rather it must also protect its networks and the functioning of electronic devices to enable cyberspace control.
- USAF must be prepared to conduct warfare in cyberspace to secure the domain at the time and place of its choosing.
- Call for an interagency commission to resolve the issues of jurisdictional authority and, if needed, author legislation for title 10 revision.
- While offense offers a distinct advantage for airpower, deterrence and defense must become co-equal propositions in cyberspace.
- Reclaim the internet, moving to a closed network, one that does not allow interaction with its civilian counterpart in any capacity or other open systems across the DOD.
- View cyberspace holistically, developing organizations and tactics to defend regardless of location, while retaining freedom of action for our forces.
- Develop system resiliency, with a layered defense in depth, that reacts to threats and sets in motion procedures for post – attack recovery.
- Develop and field self-diagnosing and self-healing systems with adequate redundant capacity for survivability.
- Develop systems to support real – time Cyberspace Situational Awareness (CSA)
- Develop a new corps of professionals capable of waging cyber warfare.
- Develop a structured professional development curriculum with a UCT school that provides the needed military education required for newly minted second lieutenants.
- Create a National Cyberspace Studies Institute (NCSI) that provides an increased understanding of cyber operations appropriate for success at the advanced ranks.
- Ensure adequate pay, attendance at the right schools – PME and weapons school – and promotion.
- Find a home/advocate for future cyber – warriors, one equal to that of air/space.
- Identify Guard and Reserve billets for cyber – professionals who are separate from active duty.
- Develop a construct to incorporate Guard and Reserve into the “fight”, either through stand – alone units or as a part of active duty units.
- Develop a Cyberspace Red Team to probe DOD networks and provide input for offensive, defensive, and counter offensive strategy.
- Develop an industry council where senior military and industry representatives convene to establish requirements and propose technological solutions.
- Partner with the private sector – universities and commercial industry to properly leverage American expertise.

No comments:
Post a Comment